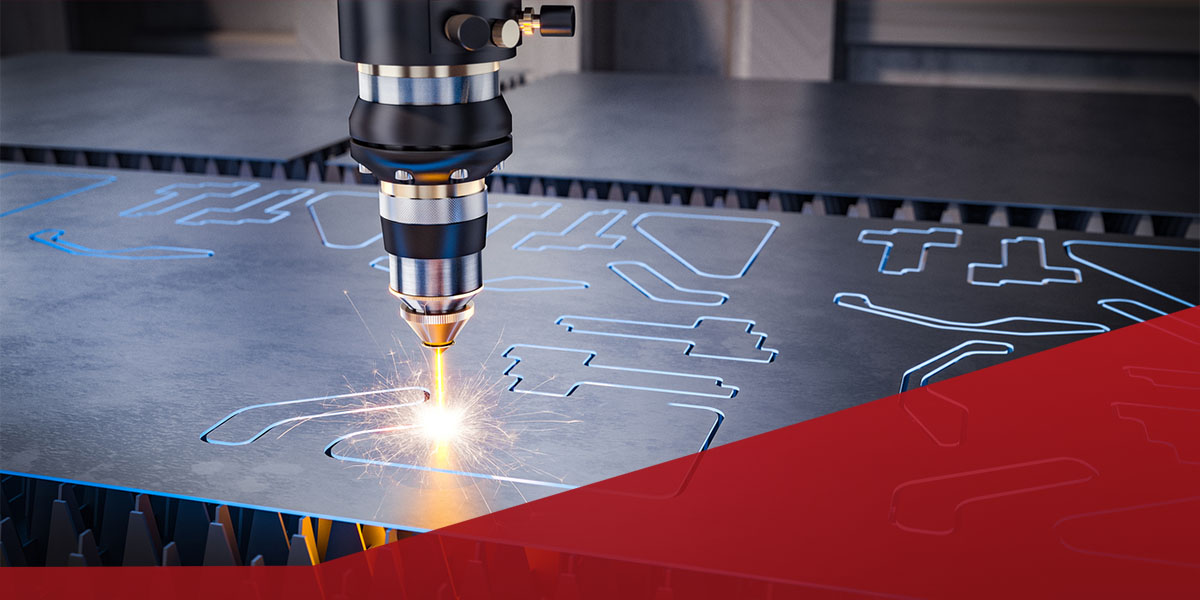
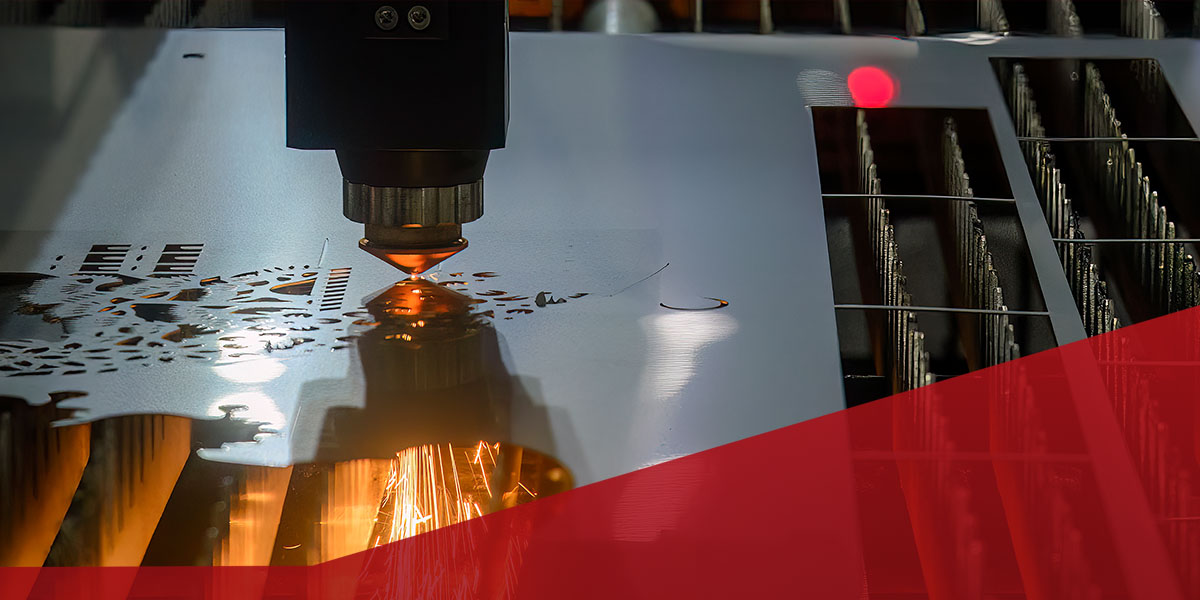
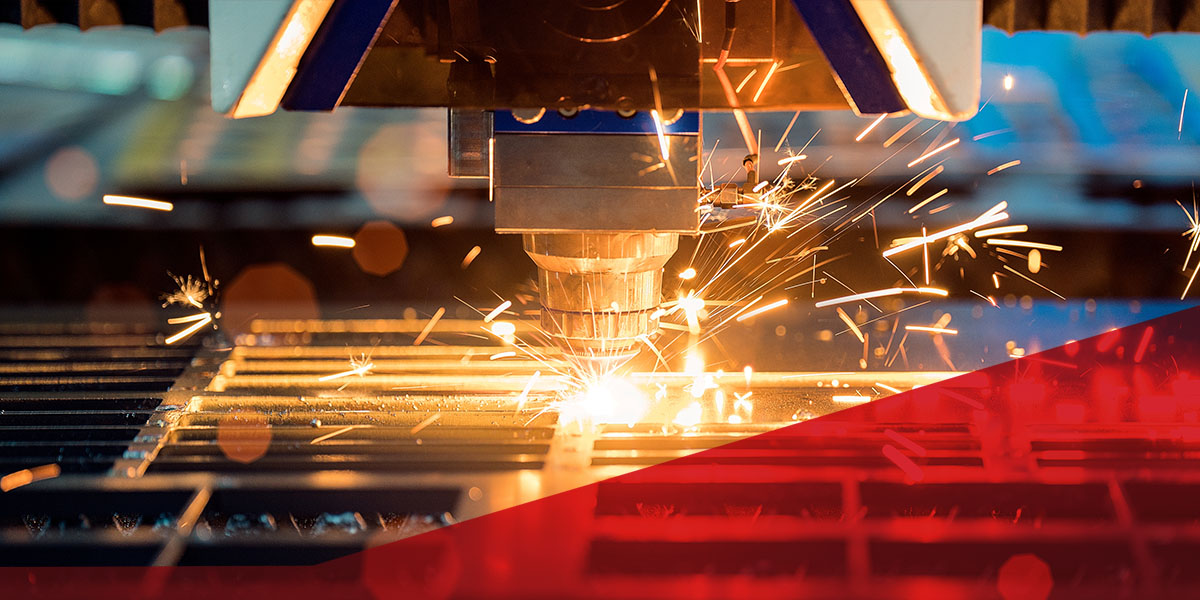
Common Laser Cutting Quality Failures and How to Fix Them
Laser cutting machines require precise parts and parameters to produce accurate results. Without the proper parts and configurations, complications such as discoloration, rough edges, raised edges and material warping can occur. Understanding how to address common cutting quality failures and where to find quality equipment and components helps ensure your cut parts and final products function properly.
Importance of Laser Cutting Quality
Laser cutting quality is important because it ensures the integrity of final products. Your laser cutting equipment must operate properly to generate precise results, so it's essential to recognize and understand common failures when they arise.
Common Laser Cutting Problems and Solutions
Learning about common equipment complications can help you prepare for them and reduce equipment downtime. Consider the following common laser cutting quality failures and how to fix them:
Burrs
Burrs are rough surfaces or raised edges that can form during laser cutting, affecting a cut part's functionality and appearance. The following complications can cause burr formation:
- Incorrect laser focus
- Excessive cutting speed
- Insufficient or incorrect assist gas pressure
The machine's beam requires a sharp focal point and low divergence to create precise cuts. You can prevent or correct burr formation with the following tips:
- Optimize beam quality and laser focus: If you notice burrs, you may need to adjust the laser diameter, beam profile, wavelength and waist, laser source stability, optical component stability, or surrounding conditions.
- Adjust the machine's laser focus position: A machine's focus position is where the laser beam's power merges to its smallest diameter. Using a machine with smooth focus point capabilities is essential for high-quality results. If your machine produces burrs, you may need to adjust the focal position to accommodate different materials or thicknesses or higher laser power. You may also need to adjust the nozzle diameter because it influences the focal point.
- Maintain a proper feed rate: You can maintain your machine's feed rate by regularly cleaning components to prevent dust accumulation and ensuring your software works correctly.
- Maintain proper air pressure and use an adequate assist gas: An assist gas, such as nitrogen, and proper air pressure are necessary to help your machine remove molten metal. Check your machine manufacturer's guidelines for the proper gas composition.
Kerf Width Variation
Kerf is the cutting slit width the laser produces, and it's important for final product quality. The proper kerf width contributes to accurate dimensions and correct parts fitment. Creating a narrow kerf enables you to nest cut patterns closely and reduce scrap metal, and consistent kerf width helps maintain a proper cutting seam and surface.
You can optimize cutting speed and increase cutting precision with the following tips:
- Adjust alignment: Adjust the cutting machine's calibration and alignment when necessary.
- Maintain the laser source and focus lens: Monitor and maintain the laser source and focus lens for consistent spot size and beam quality.
- Use a closed-loop feedback system: A closed-loop feedback system monitors and adjusts cutting specifications instantaneously to ensure consistent cutting width.
Slag or Dross Adherence
Slag or dross is the molten material that solidifies on a cut's bottom surface. If the cut surface adheres to the dross, it can affect the cut's quality and result in a need for extra post-cut cleaning.
You can prevent dross adherence with the following methods:
- Adjust cutting parameters: Optimizing cutting parameters may help reduce dross. You can increase the assist gas pressure or reduce the cutting speed and adjust as needed to prevent dross.
- Check the assist gas's flow rate and composition: Your machine's assist gas requires the proper flow rate and composition to help expel molten material during cutting.
- Perform post-cut cleaning: Adopting post-cut cleaning methods, such as sandblasting or grinding, can help remove adhered dross from the material's kerf or cutting slit.
Heat-Affected Zone
Laser cutting components and lasers generate heat, but excessive heat can cause cut edges to develop a heat-affected zone (HAZ). A HAZ can hinder a final product's performance by increasing hardness or reducing ductility.
You can prevent HAZ with the following tips:
- Minimize heat input: Optimizing cutting parameters can help minimize heat input. You may need to adjust your machine's cutting speed, laser power density and laser focus to reduce the heat its components generate.
- Use a quality machine with precise control: A high-quality machine gives you more control over parameters such as focus lens, light and the nozzle. Adjusting these small factors can help prevent HAZ.
- Complete post-cut treatments: Post-cut treatments such as stress relieving or annealing can help mitigate HAZ effects.
Discoloration
The powerful light a laser emits can oxidize or discolor cutting edges, impacting the material's surface quality and appearance. You can prevent discoloration with the following tips:
- Adjust cutting parameters: Cutting parameters such as speed, laser focus position and power can help minimize heat input to prevent discoloration.
- Adjust assist gas flow rate and composition: Making sure the assist gas has the proper flow rate and composition helps protect materials from oxidation during cutting.
- Treat materials: Implementing post-cut treatments such as surface coating or passivation helps prevent oxidation from intensifying and restores a material's original appearance.
Rough Edges or Striations
Uneven or rough edges can decrease a product's functionality and affect its appearance. You can create smooth edges with the following tips:
- Use a quality machine with precise control: Your machine should provide excellent optics and allow you to control cutting parameters precisely.
- Optimize cutting parameters: Optimizing cutting parameters, such as speed, power, assist gas pressure and feed rate, can help your laser create smooth edges.
- Treat materials: Post-cut treatment methods, such as polishing or deburring, can help smooth rough edges after cutting.
Gas Pressure Changes
Gas pressure changes can cause inconsistent cutting quality and irregularities such as angle or taper deviations. You can facilitate more consistent gas pressure with the following tips:
- Upgrade your machine: Quality laser cutting machines feature accurate, stable gas pressure control systems. If you notice significant pressure inconsistencies, you may need a new machine.
- Calibrate the gas pressure control system: Regular maintenance and calibration help ensure the system's stability and accuracy.
- Regulate gas pressure: Monitoring and regulating gas pressure when necessary is important for consistent cutting.
Thin Material Distortion or Warping
A high-power laser's intense heat input can distort or warp thin materials, affecting their appearance and functionality. You can improve thin material cutting and prevent distortion with the following tips:
- Implement a pulsing feature: Some laser cutting machines have a high-frequency, high-power pulsing feature. This feature delivers short, powerful laser pulses with pauses in between to reduce heat input and prevent warping.
- Minimize material movement: Use proper fixturing or clamping techniques to keep material stationary during cutting to prevent material movement and optimize the laser tube's performance.
- Control material temperature: Controlling material temperature with a cooling system or heat sink during cutting can prevent it from warping and maintain the laser tube's performance.
Re-Melting or Re-Solidification
Materials can re-melt or re-solidify along cut edges, resulting in uneven surfaces or rough edges. You can prevent cut edges from re-melting or re-solidifying with the following methods:
- Adjust cutting parameters: Cutting specifications such as speed, power and laser focus position prevent the laser tube from causing re-melting and re-solidification.
- Adjust the assist gas: Your assist gas should have the proper flow rate and composition to help your machine remove molten material.
- Treat materials: Post-cut treatments such as sanding or grinding can smooth uneven surfaces or rough edges.
Purchase High-Quality Laser Cutting Equipment From Alternative Parts, Inc.
The equipment you use plays a significant role in laser cutting quality and product results. With the right machines and components, you can monitor and adjust cutting parameters to prevent complications such as burrs, kerf width variation, dross adherence, HAZ, discoloration, rough edges, gas pressure changes and warping.
API offers quality laser cutting equipment and replacement parts to help you maintain accurate, consistent results. We carry industry-leading brands and offer on-site service to help you address complications efficiently. Contact us to learn more about our available parts and repair services.